If you’ve recently moved to an area where natural gas is not readily available or you’re simply looking to switch from natural gas to propane for your stove, you may be wondering how to make this conversion.
Fortunately, converting a natural gas stove to propane is a feasible DIY project that can be accomplished with the right tools and a clear understanding of the process.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the steps required to safely and effectively convert your stove from natural gas to propane.

Table of Contents
- 1 How To Convert A Natural Gas Stove To Propane?
- 2 Safety First Before The Conversion
- 2.1 1. Turn Off The Main Gas Supply
- 2.2 2. Provide Adequate Ventilation
- 2.3 3. Use Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- 2.4 4. Keep A Fire Extinguisher Nearby
- 2.5 5. No Open Flames Or Sparks
- 2.6 6. Have A Gas Detector
- 2.7 7. Read Instructions Carefully
- 2.8 8. Double-Check Connections
- 2.9 9. Stay Informed And Seek Help If Needed
- 3 Gather Your Tools And Materials
- 4 Step-By-Step Process To Convert A Natural Gas Stove To Propane
- 5 How Much Does It Cost To Convert A Gas Stove To Propane?
- 6 Gas Stove To Propane Conversion Kit
- 7 What Happens If You Don’t Convert Natural Gas To Propane?
- 8 Is It Better To Be On Natural Gas Or Propane?
- 9 Is There A Difference Between A Propane Stove And A Natural Gas Stove?
- 10 Is Propane Twice As Expensive As Natural Gas?
- 11 What Burns Hotter Propane Or Natural Gas?
- 12 What Happens If You Run A Natural Gas Furnace On Propane?
- 13 Maintenance And Troubleshooting For Your Propane Gas Stove
- 14 Benefits Of Propane Stoves Over Natural Gas Stoves
- 15 Final Verdict On Converting A Natural Gas Stove To Propane
- 16 FAQs
- 16.1 What Is The Primary Difference Between Natural Gas And Propane Stoves?
- 16.2 Can I Convert Other Gas Appliances To Propane?
- 16.3 Is It Safe To Perform The Conversion Myself?
- 16.4 How Often Should I Perform Maintenance On My Propane Stove?
- 16.5 Are There Any Government Regulations Regarding Gas Stove Conversions?
How To Convert A Natural Gas Stove To Propane?
Converting a natural gas stove to propane in a DIY approach involves turning off the gas supply, disconnecting the stove, and replacing the gas orifices with propane-specific ones. You’ll also need to adjust the regulator for propane use and perform a thorough leak test to ensure there are no gas leaks.
Refer below for a complete step-by-step process.
Also Read – Why Is My Gas Stove Not Clicking?
But before that, let’s take some safety precautions.
Safety First Before The Conversion
When converting a natural gas stove to propane, safety should always be your top priority. Working with gas appliances carries inherent risks, and any mistakes can have severe consequences. Here’s a detailed elaboration on the safety precautions you should take:
1. Turn Off The Main Gas Supply
Before you begin any work on your gas stove, locate the main gas supply valve in your home and ensure it is turned off. This step is crucial because it prevents any gas flow to the appliance you are working on. The main gas supply valve is typically located near the gas meter or the gas entry point into your home.
2. Provide Adequate Ventilation
Proper ventilation in your kitchen is vital during this process. Gas appliances produce potentially harmful fumes, and having good airflow helps prevent the buildup of these gases. Open windows and doors, use fans or even consider working outdoors if possible. Adequate ventilation significantly reduces the risk of gas-related accidents.
3. Use Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear the necessary personal protective equipment (PPE) when working on gas appliances. Safety glasses protect your eyes from potential debris or gas, while gloves protect your hands. In some cases, a dust mask or respirator may be necessary, especially if you are working in a confined or poorly ventilated space.
4. Keep A Fire Extinguisher Nearby
Accidents can happen, even when taking all precautions. Having a fire extinguisher within reach is a wise precaution. Make sure the fire extinguisher is suitable for use on gas fires, and that you know how to operate it. Familiarize yourself with its location and how to access it quickly.
5. No Open Flames Or Sparks
During the conversion process, avoid open flames or sparks near the work area. This means no smoking, no open flames from candles, and no electrical tools that could potentially generate sparks. A small spark can ignite gas fumes, leading to a dangerous situation.
6. Have A Gas Detector
Consider investing in a gas detector, which can alert you to the presence of gas leaks. These detectors are especially useful in enclosed spaces where gas can accumulate without being easily noticed. A gas detector can provide an early warning, allowing you to address any leaks promptly.
7. Read Instructions Carefully
Whether you’re using a propane conversion kit or following the manufacturer’s instructions, read all documentation carefully before starting the conversion. Understanding the steps and requirements thoroughly can help you avoid errors that may compromise safety.
8. Double-Check Connections
Before turning the gas supply back on and testing your stove, double-check all connections. Ensure that all fittings are tight and secure, and there are no loose components. A small gas leak can lead to a dangerous situation over time.
9. Stay Informed And Seek Help If Needed
If you encounter any issues or feel unsure about any aspect of the conversion process, do not hesitate to seek professional assistance. Gas-related work can be complex, and it’s better to have a trained technician resolve any doubts or problems.
Also Read – Why Gas Stove Won’t Light But Smells Gas?
Gather Your Tools And Materials
Before you embark on the process of converting your natural gas stove to propane, it’s essential to gather all the necessary tools and materials. Having the right equipment at hand ensures a smooth and efficient conversion process. Here’s a list of the tools and materials you’ll need:

Tools Needed
- Wrenches And Pliers: You’ll require an adjustable wrench and pliers to safely disconnect and reattach gas lines and fittings. These tools ensure a secure and leak-free connection.
- Screwdrivers: Keep a set of flat-head and Phillips-head screwdrivers on hand. They may be needed to remove screws securing various parts of your stove.
- Pipe Thread Sealant: A high-quality pipe thread sealant, often referred to as “pipe dope” or “pipe joint compound,” is crucial for sealing threaded connections. It helps prevent gas leaks at the joints.
- Soapy Water (For Leak Testing): A solution of soapy water is an effective way to detect gas leaks. You’ll use this to check all connections for any signs of escaping gas.
- Propane Pressure Regulator: This is a critical component for adjusting the gas pressure to the appropriate level for your propane stove. Ensure you have the correct regulator for your stove model.
Also Read – How To Fix A Yellow Flame On A Gas Stove?
Procuring The Propane Conversion Kit
Contact your stove’s manufacturer or a reputable appliance parts supplier to obtain a propane conversion kit designed specifically for your stove model. This kit is essential for a successful conversion and typically includes the following components:
- Propane Orifices: These small brass pieces control the flow of gas to the burners. The kit should include orifices suitable for propane use.
- Conversion Instructions: The kit should come with clear and detailed instructions on how to perform the conversion. Follow these instructions carefully to ensure a safe and effective process.
- Additional Hardware: Depending on your stove’s design, the kit may include any additional hardware or components required for the conversion.
Step-By-Step Process To Convert A Natural Gas Stove To Propane
Step 1: Shut Off the Gas Supply
Before you can begin the process of converting your natural gas stove to propane, it’s crucial to shut off the gas supply to ensure your safety during the conversion. Here are the steps to follow:
- Locate the Main Gas Supply Valve: The main gas supply valve is typically located near the gas meter or the point where the gas line enters your home. It’s essential to know the exact location of this valve as it controls the flow of natural gas to your entire house.
- Turn Off the Valve: Using an adjustable wrench, turn the valve to the “off” position. The valve handle is usually perpendicular to the gas line when it’s in the “off” position. This action will completely shut off the supply of natural gas to your home.
- Verify the Gas Flow Is Off: To ensure that the gas supply is indeed turned off, you can check your gas stove or any other gas appliances in your home. Try to ignite a burner on your stove. If the gas supply is successfully shut off, the burner should not light.
- Leave the Valve in the Off Position: Leave the main gas supply valve in the “off” position throughout the entire conversion process. This precaution ensures that no natural gas flows into the stove while you are working on it, minimizing the risk of accidents.
It’s essential to emphasize that turning off the gas supply is a critical safety measure. Gas is highly flammable, and any inadvertent leaks during the conversion process can lead to dangerous situations.
By shutting off the gas supply at the main valve, you create a safe environment in which to perform the necessary modifications to your stove.
Also Read – Do Gas Stoves Turn Off Automatically?
Step 2: Prepare The Stove
Before you can proceed with converting your natural gas stove to propane, you need to prepare the stove for the modification process. This involves several steps to ensure safe and effective conversion. Here’s how to prepare your stove:
- Removing Grates And Burners: Begin by removing the grates and burners from your stove. These components can obstruct your access to the gas orifices and other parts that need to be modified. Gently lift them off and set them aside in a safe place.
- Accessing The Gas Orifices: Once the grates and burners are removed, you’ll have a clear view of the gas orifices. These are small brass fittings that control the flow of gas to the burners. You’ll need to replace these orifices with ones designed for propane use.
- Disconnect The Gas Supply: Before proceeding, double-check that the main gas supply is still turned off. It should remain in the “off” position throughout the conversion process. Also, ensure there are no gas leaks or lingering gas smells in the vicinity.
- Cleaning The Stove: Take this opportunity to clean the stove thoroughly. Wipe down the stove’s surface, including the cooktop, with a mild detergent and water. Cleaning now will make it easier to work on the stove and ensure there are no obstructions or debris when you access the gas orifices.
- Organize Your Workspace: Arrange your tools, the propane conversion kit, and any additional materials you may need in an organized and easily accessible manner. This will save you time and help prevent accidents during the conversion.
By preparing the stove in this manner, you create a safe and efficient work environment for the subsequent steps of the conversion process.
Step 3: Replace The Gas Orifices
One of the critical steps in converting your natural gas stove to propane is replacing the gas orifices. These small brass components control the flow of gas to the burners and are specific to the type of gas you’re using.

Here’s how to replace the gas orifices with ones designed for propane use:
- Selecting The Correct Orifices: Refer to the instructions provided in your propane conversion kit. It should contain a set of propane orifices suitable for your stove model. These orifices are designed to allow the correct flow of propane gas, which differs from natural gas in terms of pressure and combustion characteristics.
- Safety First: Before you begin, reiterate the importance of safety. Ensure that the main gas supply to your stove is turned off and that there are no lingering gas fumes in the area. Use appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses and gloves.
- Access The Orifices: As you prepared the stove in the previous step, you should have clear access to the gas orifices. They are typically located beneath each burner on the cooktop. Carefully remove any burner covers or shields to expose the orifices.
- Remove The Existing Orifices: Using a wrench or pliers, gently unscrew the existing natural gas orifices from each burner. Be cautious not to damage the orifice or the surrounding components. Place the removed orifices in a safe location; you may need them in the future if you ever switch back to natural gas.
- Install The Propane Orifices: Take the propane orifices provided in your conversion kit and screw them securely into the same positions where you removed the natural gas orifices. Use the appropriate tools to ensure a snug fit, but avoid overtightening, as it could damage the orifices or the burners.
- Double-Check The Connections: After installing the propane orifices, double-check all the connections. Ensure that they are tight and secure. Loose connections can lead to gas leaks, which can be hazardous.
- Replace Burner Covers And Shields: Once all the propane orifices are installed, reattach any burner covers or shields that you removed earlier. These components help protect the orifices and ensure proper burner operation.
Also Read – How Long Can You Leave An Electric Stove On?
Step 4: Adjust The Regulator
Once you’ve replaced the gas orifices with those suitable for propane and ensured that all connections are secure, the next crucial step in converting your natural gas stove to propane is adjusting the regulator.
The regulator controls the pressure of the gas supplied to your stove, ensuring it’s at the correct level for safe and efficient propane operation. Here’s how to adjust the regulator:
- Locate The Regulator: The gas regulator is typically located at the back of your stove, near the point where the gas line connects to the appliance. It’s essential to know where it is as you’ll need to access it for the adjustment.
- Check The Regulator Settings: Refer to the instructions provided in your propane conversion kit or the stove’s manual to determine the correct regulator setting for propane. The kit should include details on the specific adjustments needed for your stove model.
- Adjust The Regulator: Using a wrench or pliers, adjust the regulator to the prescribed setting for propane gas. This typically involves turning a screw or adjusting a dial on the regulator. Follow the kit’s instructions carefully to ensure that you set the pressure correctly.
- Verify The Adjustment: After adjusting, double-check that the regulator is set to the correct pressure for propane. Proper regulator adjustment is crucial for safe stove operation, so take your time and ensure accuracy.
- Secure The Regulator: Once you’ve adjusted the regulator to the correct pressure, secure it in place to prevent accidental changes. This might involve tightening a locking nut or fastening a screw to keep the adjustment in position.
- Replace Any Covers: If you remove any covers or panels to access the regulator, be sure to reattach them securely. These covers protect the regulator and other components, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
Adjusting the regulator is a critical step in the conversion process, as it ensures that the propane supply to your stove is at the right pressure for safe and efficient cooking.
Step 5: Perform A Leak Test
Performing a leak test is a crucial safety measure when converting your natural gas stove to propane. It helps ensure that all connections are secure and that there are no gas leaks that could lead to potentially hazardous situations. Here’s how to conduct a leak test:
- Prepare The Soapy Water Solution: Create a soapy water solution by mixing a small amount of dishwashing soap with water in a spray bottle or a bowl. The soap solution will be used to identify any gas leaks.
- Turn On The Gas Supply: Carefully turn on the main gas supply to your stove. Ensure that the regulator is properly adjusted and that there are no obstructions in the gas lines.
- Apply The Soapy Water: With the gas supply turned on, systematically apply the soapy water solution to all gas connections and fittings. This includes:
- Gas line connections: Check where the gas line connects to the stove and any other gas-related connections.
- Orifices: Apply the solution to the newly installed propane orifices and their fittings.
- Regulator and adjustments: Inspect the regulator and the areas around any adjustments you make. Apply the solution here as well.
- Observe For Bubbles: Watch closely for any signs of bubbles forming at the connections as you apply the soapy water solution. If you see bubbles, it indicates a gas leak. Gas leaks can be dangerous, so take any sign of a leak seriously.
- Addressing Leaks: If you detect a gas leak, follow these steps:
- Turn off the Gas Supply: Immediately turn off the main gas supply to your stove to stop the flow of gas.
- Tighten Connections: If the leak is coming from a loose connection, use the appropriate tools to tighten it securely.
- Reapply the Solution: After addressing the issue, reapply the soapy water solution to the area to confirm that the leak has been resolved.
- Seek Professional Help: If you’re unable to stop the leak or if it persists, do not attempt to proceed further. Instead, contact a qualified gas technician or plumber to assess and repair the issue.
- Repeat The Test: Perform the leak test thoroughly, checking all connections and fittings. Be meticulous, as even a small leak can be dangerous. Continue testing until you are confident that there are no leaks present.
- Confirm A Leak-Free System: Once you have completed the leak test and are certain that there are no gas leaks, you can proceed to the next steps in the conversion process with confidence.
- Safety First: Always prioritize safety when working with gas appliances. If you have any doubts about the integrity of your gas connections or if you are unsure how to perform a leak test, seek professional assistance. Gas-related projects should be handled with care and expertise to ensure the safety of yourself and your home.
By performing a thorough leak test, you can ensure that your converted propane stove operates safely and without the risk of gas leaks.
Also Read – How Hot Do Electric Stove Burners Get?
Step 6: Reassemble And Test The Stove
After successfully replacing the gas orifices, adjusting the regulator, and performing a leak test, it’s time to reassemble your stove and conduct a series of tests to ensure that the conversion from natural gas to propane has been completed effectively.
Here are the steps to reassemble and test your stove:
- Reattaching Burners And Grates: Begin by reattaching the burners and grates to your stove. Carefully place each component back in its original position, making sure it fits snugly. Take your time to ensure that everything is properly aligned.
- Secure All Components: Check that all components, including the burners, grates, and any covers or shields, are securely fastened in place. Loose components can affect the stove’s performance and safety.
- Turn On The Gas Supply: Gently turn on the main gas supply to your stove. Be sure to do this slowly to allow the gas to flow gradually.
- Ignite The Burners: One by one, attempt to ignite each burner on your stove. If your stove has an electric ignition system, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for lighting the burners. Ensure that all burners light evenly and produce a blue flame.
- Check For Proper Flame: As each burner ignites, observe the flame. A blue flame is an indicator of proper combustion. If you notice any irregularities, such as uneven flames or yellow flames, it could signal an issue that needs further attention.
- Test All Burners: Test each burner individually to ensure they all function correctly. Pay close attention to any variations in flame quality or burner performance.
- Adjust Flame Settings (If Necessary): If you notice any irregularities in the flame, refer to your stove’s manual or the instructions provided with the propane conversion kit to make any necessary adjustments. This might involve fine-tuning the air-to-fuel mixture for optimal performance.
- Conduct A Test Cook: To fully verify the stove’s functionality, cook a simple dish, such as boiling water or sautéing vegetables. This will allow you to assess how well the stove operates with the new propane setup.
- Monitor For Any Issues: While cooking, pay attention to any unusual odors, sounds, or performance issues. If you detect anything out of the ordinary, discontinue use and investigate the problem further.
- Regular Maintenance: After successful testing, it’s essential to establish a routine maintenance schedule for your propane stove. Regular cleaning and inspections will help keep it operating efficiently and safely.
By reassembling and testing your stove methodically, you can confirm that the conversion process has been completed successfully.
Proper ignition, even flames, and consistent burner performance are all indicators of a well-executed conversion from natural gas to propane.
If you encounter any persistent issues or concerns during testing, it’s advisable to consult the stove’s manual or seek professional assistance to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Also Read – How To Fix A Yellow Flame On A Gas Stove?
How Much Does It Cost To Convert A Gas Stove To Propane?
The cost of converting a gas stove to propane can vary depending on several factors, including the type of stove, the availability of conversion kits, and whether you choose to do the conversion yourself or hire a professional.
Here are some cost considerations for converting a gas stove to propane:
- Propane Conversion Kit: The most significant cost is typically the propane conversion kit itself. These kits include the necessary orifices and components to adapt your stove for propane use. The price of a conversion kit can range from $30 to $100 or more, depending on the stove model and the brand of the kit.
- Labor Costs (If Hiring A Professional): If you opt to hire a professional plumber or appliance technician to perform the conversion, you will incur labor costs. Labor charges can vary widely depending on your location and the complexity of the conversion. Expect to pay anywhere from $100 to $300 or more for labor.
- Additional Materials: In addition to the conversion kit, you may need some additional materials, such as pipe thread sealant, tools, and safety equipment. These costs can vary but are generally minimal compared to the kit and labor expenses.
- Gas Supply Line Modifications:
- If your existing natural gas supply line does not have a propane connection, you may need to invest in a propane tank and associated equipment.
- The cost of a propane tank can range from a few hundred dollars to over a thousand dollars, depending on the size and type of tank you choose.
- Installation costs for the tank and gas lines can vary significantly based on your location and specific requirements.
- Diy Vs. Professional Installation: If you have the necessary skills and tools, you can perform the conversion yourself, which can save on labor costs. However, if you’re not confident in your abilities or want to ensure the conversion is done safely, hiring a professional is advisable.
- Permits And Inspections: Depending on your local regulations, you may need permits or inspections for the gas stove conversion. These costs can vary widely based on your location and the specific requirements of your local authorities.
- Maintenance And Safety Checks: It’s essential to include ongoing maintenance costs in your budget. Regular maintenance ensures that your propane stove operates safely and efficiently. This may involve cleaning, inspections, and occasional component replacement.
Also Read – Orange Flame On The Gas Stove: Causes And Fixes
Gas Stove To Propane Conversion Kit
A gas stove-to-propane conversion kit is an essential component when transitioning from natural gas to propane as your cooking fuel. This kit typically includes specialized orifices, a regulator, and detailed instructions for adjusting your stove to ensure safe and efficient propane operation.
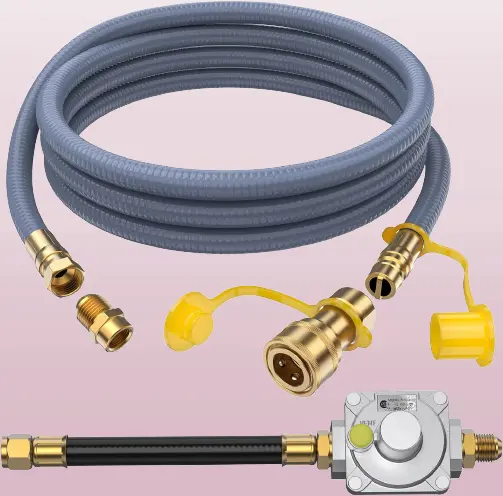

Here’s a breakdown of what you can expect from a gas stove to propane conversion kit:
- Propane Orifices: These are small, precisely engineered openings that control the flow of propane gas to the stove’s burners. The conversion kit includes orifices specifically designed for propane, which are smaller than those used for natural gas. Replacing the existing orifices with propane orifices ensures the correct air-to-fuel mixture for proper combustion.
- Regulator: The kit usually includes a propane regulator, which is responsible for reducing the high pressure of propane in the tank to a lower pressure suitable for your stove. Proper regulator installation and adjustment are crucial for safety and efficient operation.
- Conversion Instructions: Comprehensive instructions are provided to guide you through the conversion process. These instructions typically cover the step-by-step procedure for disassembling your stove, replacing orifices, adjusting the regulator, and conducting leak tests to ensure a safe conversion.
- Safety Considerations: The kit may also include safety information and guidelines to help you understand the potential risks and precautions associated with converting your stove. Following safety recommendations is paramount to prevent accidents and hazards.
- Additional Components (If Required): Depending on your stove model and the conversion kit, there may be additional components included, such as gaskets, fittings, or adapters, to ensure a proper and secure conversion.
Keep in mind that using a gas stove to propane conversion kit should only be done by individuals with a strong understanding of gas systems and safety precautions.
If you are uncertain about any aspect of the conversion process or lack the necessary expertise, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance to ensure a safe and successful conversion from natural gas to propane.
Also Read – What Happens If You Use Propane On A Natural Gas Stove?
What Happens If You Don’t Convert Natural Gas To Propane?
If you don’t convert a natural gas appliance, such as a stove, to propane when it’s intended to run on propane, several significant issues and safety risks can arise:
- Inefficient Combustion:
- Natural gas and propane have different combustion properties, including pressure and air-to-fuel ratios.
- If you use a natural gas appliance with propane without converting it, it will not burn efficiently.
- This can lead to incomplete combustion, producing excessive carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless and odorless gas that can be lethal in high concentrations.
- Flame Irregularities: The orifices in natural gas appliances are sized for the lower pressure and higher flow rate of natural gas. When you use propane with these orifices, the flame will likely be irregular, with yellow tips and a less stable burn. This can result in uneven heating, poor cooking performance, and even burner malfunction.
- Safety Hazards: The improper use of propane in a natural gas appliance can lead to gas leaks, which are highly dangerous due to propane’s flammability. A gas leak can result in fire or explosions if ignited.
- Appliance Damage: The use of propane in a natural gas appliance can cause damage to the appliance itself. Propane burns at a higher temperature, and the increased heat can harm internal components, including burners, valves, and regulators. Over time, this can lead to the appliance’s deterioration and reduced lifespan.
- Voided Warranties: Attempting to use propane in a natural gas appliance without proper conversion typically voids the manufacturer’s warranty. This means that if the appliance is damaged or malfunctions, you won’t be eligible for repairs or replacements under warranty.
- Legal And Safety Violations: In many regions, using propane in a natural gas appliance without conversion can be illegal due to safety and environmental concerns. Violating local regulations can result in fines and penalties.
- Health Risks: Inefficient combustion of propane in a natural gas appliance can produce harmful byproducts, including carbon monoxide. Prolonged exposure to elevated levels of carbon monoxide can lead to health issues, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, and, in severe cases, carbon monoxide poisoning.
Also Read – Master Medium Heat On A Stove
Is It Better To Be On Natural Gas Or Propane?
The choice between natural gas and propane depends on various factors, including your location, energy needs, and personal preferences. Both natural gas and propane have their advantages and disadvantages, so it’s essential to consider your specific circumstances when determining which is better for you.
Here’s a comparison of the two:
Natural Gas
- Lower Cost: Natural gas is often less expensive than propane, making it a cost-effective choice for heating, cooking, and other applications.
- Convenient Supply: Natural gas is delivered through underground pipelines, so you don’t need to worry about refilling tanks or running out of fuel.
- Clean-Burning: Natural gas is a relatively clean-burning fossil fuel, producing fewer emissions than some other energy sources.
- Continuous Supply: With a natural gas connection, you have a continuous supply of gas, so you don’t need to monitor or schedule deliveries.
- Limited Storage Needs: Since natural gas is supplied directly through pipelines, you don’t need to allocate space for storage tanks.
Propane
- Portability: Propane is portable and can be used in areas without access to natural gas pipelines, making it suitable for outdoor cooking, RVs, and remote locations.
- Energy Independence: Propane tanks provide an independent energy source, which can be beneficial in areas prone to power outages.
- High Energy Density: Propane has a high energy density, meaning it can produce a significant amount of heat in a compact space, making it ideal for space heating and water heating.
- Versatility: Propane can power a wide range of appliances, including stoves, ovens, grills, heaters, and generators.
- Environmentally Friendly Options: Propane is available as a green or bio propane variant, produced from renewable sources, which can reduce its environmental impact.
Considerations
- Availability: The availability of natural gas and propane depends on your location. In rural areas or places without natural gas pipelines, propane may be the more accessible option.
- Installation Costs: Installing natural gas pipelines can be expensive, while propane tanks and systems often have lower upfront costs.
- Energy Efficiency: The energy efficiency of appliances designed for natural gas or propane may vary. Ensure your appliances are optimized for the fuel you choose.
- Environmental Impact: While natural gas is cleaner burning than some fossil fuels, it still produces greenhouse gas emissions. Propane’s environmental impact can be reduced by using biopropane or ensuring efficient combustion.
Ultimately, the choice between natural gas and propane should align with your specific needs, cost considerations, and access to infrastructure. It’s advisable to consult with energy professionals and consider local regulations when making your decision.
Additionally, think about your long-term energy needs and any potential changes in your location or lifestyle that might influence your choice.
Also Read – Should A Slow Cooker Simmer On Low?
Is There A Difference Between A Propane Stove And A Natural Gas Stove?
Yes, there are differences between a propane stove and a natural gas stove, primarily related to the type of fuel they use and their compatibility with that fuel source. Here are the key distinctions between the two:
1. Fuel Type:
- Propane Stove: A propane stove is designed to operate specifically on propane gas. Propane is a hydrocarbon gas stored in pressurized tanks, and it has different combustion characteristics, pressure, and energy content compared to natural gas.
- Natural Gas Stove: A natural gas stove is designed to run on natural gas, which is primarily composed of methane. Natural gas is typically delivered to homes and businesses through underground pipelines.
2. Orifices:
- Propane Stove: Propane stoves come equipped with orifices (small openings) that are sized to accommodate the specific flow and pressure of propane gas. These orifices are smaller than those used for natural gas to ensure proper combustion.
- Natural Gas Stove: Natural gas stoves have larger orifices calibrated for the lower pressure and higher flow rate of natural gas.
3. Flame Characteristics:
- Propane Stove: When burning propane, the flame is typically blue with yellow tips. Propane burns hotter and has a higher energy content than natural gas, resulting in a more intense flame.
- Natural Gas Stove: Natural gas burns with a primarily blue flame. It produces less heat energy per unit volume compared to propane.
4. Energy Content:
- Propane Stove: Propane contains more energy per unit volume than natural gas. As a result, propane stoves can often heat and cook more efficiently.
- Natural Gas Stove: Natural gas has a lower energy content compared to propane. While it’s still a suitable fuel for cooking and heating, it may be less efficient in certain applications.
5. Storage And Delivery:
- Propane Stove: Propane is typically stored in portable tanks that need to be periodically refilled or exchanged. It’s commonly used in outdoor grills, RVs, and portable stoves.
- Natural Gas Stove: Natural gas is delivered directly to homes and businesses through underground pipelines. Users have a continuous supply without the need for refilling tanks.
6. Conversion:
- Propane To Natural Gas: Some propane stoves can be converted to natural gas by replacing orifices and making adjustments. However, this should be done carefully and often requires professional assistance.
- Natural Gas To Propane: Similarly, some natural gas stoves can be converted to use propane with the appropriate conversion kit, including changing orifices and adjusting the regulator. This conversion also typically requires professional expertise.
So, the primary difference between a propane stove and a natural gas stove lies in their fuel source, orifices, flame characteristics, and energy content. It’s essential to use the correct type of stove for the corresponding gas source to ensure safety, efficiency, and proper combustion.
If you’re considering converting between the two fuels, it’s crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines and seek professional assistance to make the necessary adjustments safely and effectively.
Also Read – Is Simmer Lower Than Low?
Is Propane Twice As Expensive As Natural Gas?
The cost of propane compared to natural gas can vary significantly depending on several factors, including your location, market conditions, and the time of year.
Propane is generally more expensive than natural gas on an energy-equivalent basis, but it’s essential to understand that the price difference is not always a fixed multiple.
Here are some key considerations:
- Energy Content: Propane contains more energy per unit volume than natural gas. In other words, a given volume of propane will provide more heat energy compared to the same volume of natural gas.
- Pricing Mechanisms: Propane prices can be more volatile than natural gas prices. Propane prices are often influenced by factors such as supply and demand, weather conditions, and global energy markets. Natural gas prices can also fluctuate but are typically more stable due to long-term contracts and infrastructure investments.
- Geographic Variations: The price difference between propane and natural gas can vary by region. Some areas may have lower propane prices compared to others, while natural gas may be more readily available and affordable in specific regions.
- Seasonal Variations: Propane prices tend to be higher during the winter heating season when demand is at its peak. Natural gas prices can also fluctuate seasonally but may not experience the same level of increase during colder months.
- Infrastructure Costs: The cost of installing and maintaining natural gas pipelines can be significant, especially in rural or remote areas. In such cases, using propane might be a more cost-effective option.
- Efficiency Considerations: The energy efficiency of your appliances can also impact costs. If you have highly efficient propane appliances, you may be able to offset some of the cost difference through lower energy consumption.
While propane is generally more expensive than natural gas on an energy-equivalent basis, the exact price difference can vary widely. It’s advisable to check local propane and natural gas prices in your area and consider factors such as infrastructure availability, energy efficiency, and seasonal variations when determining the cost-effectiveness of one fuel source over the other.
Additionally, assessing your specific energy needs and usage patterns will help you make an informed decision regarding which fuel source is more economical for your circumstances.
Also Read – How To Simmer On An Electric Stove?
What Burns Hotter Propane Or Natural Gas?
Propane burns hotter than natural gas when comparing energy content on an equal volume basis. The key reason for this difference in heat output is the energy density of the two gases.
Here’s a brief explanation of why propane burns hotter:
- Propane:
- Propane is a hydrocarbon gas that is stored in a liquid state under pressure. When it’s burned, it converts from a liquid to a gas and releases a significant amount of heat energy.
- Propane has a higher energy content per unit volume compared to natural gas. This means that for the same volume of propane and natural gas, propane will produce more heat when burned.
- The energy content of propane is approximately 2,500 to 2,800 British Thermal Units (BTUs) per cubic foot (ft³).
- Natural Gas:
- Natural gas primarily consists of methane and is delivered to homes and businesses through underground pipelines.
- While natural gas is a clean-burning fuel, it has a lower energy content per unit volume compared to propane.
- The energy content of natural gas typically ranges from 900 to 1,100 BTUs per cubic foot (ft³).
Because of the higher energy content of propane, it can produce a hotter flame when burned, making it suitable for applications where high heat output is required, such as cooking, space heating, and industrial processes.
However, it’s essential to use the appropriate fuel for the equipment and appliances you have, as they are designed to operate efficiently with the specific fuel they are intended for.
Converting equipment from one fuel source to another should be done following manufacturer guidelines and with professional expertise to ensure safe and effective operation.
Also Read – What Temperature Is Simmer On An Electric Stove?
What Happens If You Run A Natural Gas Furnace On Propane?
Running a natural gas furnace on propane without proper conversion can lead to several significant issues and safety concerns due to the differences between the two types of gas. It’s crucial to understand that natural gas and propane have distinct properties and combustion characteristics.
Here’s what can happen if you attempt to run a natural gas furnace on propane without conversion:
- Incomplete Combustion: Propane has a higher energy content and burns hotter than natural gas. If you use propane in a natural gas furnace without adjusting the orifices and combustion settings, the combustion process will be incomplete. This can result in a range of problems, including:
- Uneven Or Flickering Flames: The flame may be irregular, leading to uneven heating and poor combustion efficiency.
- Carbon Monoxide (Co) Production: Incomplete combustion generates higher levels of carbon monoxide, a colorless and odorless gas that can be harmful or even lethal if it accumulates indoors.
- Overheating And Damage: Propane burns at a higher temperature than natural gas. This increased heat can cause damage to the furnace’s heat exchanger, burners, and other internal components. Over time, this can result in costly repairs or the need for a furnace replacement.
- Flame Rollout: Running propane in a natural gas furnace can lead to flame rollout, where the flame escapes from the combustion chamber into the surrounding area. This is a severe safety hazard that can result in fires or explosions.
- Safety Risks: Propane has different pressure requirements than natural gas. If the furnace’s gas valve, regulator, and other components are not adjusted to accommodate propane, it can create unsafe operating conditions, potentially causing gas leaks, fires, or other hazards.
- Voided Warranty: Using propane in a natural gas furnace without proper conversion typically voids the manufacturer’s warranty. This means that any damage or malfunctions resulting from the use of propane may not be covered for repair or replacement.
So, attempting to run a natural gas furnace on propane without the necessary conversion is extremely dangerous and can result in incomplete combustion, carbon monoxide production, damage to the furnace, safety risks, and voided warranties.
If you want to use propane in a furnace designed for natural gas, it’s essential to have a professional technician properly convert the furnace to ensure safe and efficient operation. Safety should always be the top priority when working with gas appliances.
Also Read – What Does Simmer Look Like?
Maintenance And Troubleshooting For Your Propane Gas Stove
Maintaining your propane stove and promptly addressing any issues or concerns is crucial to ensure its safe and efficient operation. In this section, we’ll discuss routine maintenance tasks and common troubleshooting tips for your converted stove:
Regular Maintenance Tips
- Clean Regularly: Clean the cooktop, burners, and grates regularly using mild detergent and water. Avoid using abrasive cleaners that could damage the surface.
- Inspect For Wear: Periodically inspect all components for signs of wear or damage. Pay attention to the condition of the burners, orifices, and gas lines.
- Check For Gas Leaks: Continue to perform occasional leak tests using a soapy water solution to ensure there are no gas leaks in the connections or fittings.
- Clean Burner Ports: If you notice uneven flames or poor burner performance, clean the burner ports with a soft brush or a toothbrush. Clogged ports can disrupt the gas flow.
- Lubricate Valves (If Applicable): If your stove has valve controls, consider applying a small amount of silicone-based lubricant to keep them operating smoothly.
- Inspect Gas Line: Examine the gas line for any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Replace any compromised sections promptly.
- Keep Ventilation Clear: Ensure that the area around the stove is well-ventilated at all times. Proper ventilation helps prevent the buildup of gas fumes.
Also Read – Can Induction Pans Be Used On Gas Stoves?
Common Issues And Solutions
- Yellow Flames: Yellow flames are often a sign of incomplete combustion. This can be caused by an improper air-to-fuel mixture. Check the orifices and adjust them as needed to ensure a blue flame.
- Uneven Flames: If flames are uneven or inconsistent, clean the burner ports to remove any debris or blockages. Additionally, ensure that the burners and orifices are properly aligned.
- Gas Smell: If you detect a persistent gas smell, immediately shut off the gas supply and check for leaks using a soapy water solution. Address any leaks promptly and do not use the stove until the issue is resolved.
- Ignition Problems: If burners do not ignite properly, ensure that the electric ignition system is functioning correctly. Clean the ignition components if necessary. For manual ignition stoves, ensure the pilot light is lit.
- Burner Control Issues: If you have trouble adjusting burner flames or controlling temperatures, check the regulator settings and adjust them according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Inconsistent Heating: If you notice uneven heating or temperatures, consider calibrating the burner controls if your stove allows it. This can help achieve more precise temperature settings.
- Strange Noises: Unusual noises can indicate issues with gas flow or components. If you hear hissing sounds or clicking noises, turn off the gas supply immediately and seek professional assistance.
- Pilot Light Problems: If your stove has a pilot light, ensure it remains lit. If it continually extinguishes, it may require cleaning or adjustment. Refer to your stove’s manual for specific guidance.
- Low Flame: A low flame can result from a partially closed gas valve. Ensure that the burner controls are fully open for proper flame height.
Also Read – Can Clay Pots Be Used On The Gas Stove?
Benefits Of Propane Stoves Over Natural Gas Stoves
Propane stoves offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for both indoor and outdoor cooking. Whether you’re considering converting your stove or purchasing a new one, understanding the benefits of propane stoves can help you make an informed decision.
Here are some of the key advantages:
- Clean-Burning Fuel: Propane is a clean-burning fuel, producing fewer emissions than other fossil fuels. When you cook with propane, you reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to better air quality.
- Precise Temperature Control: Propane stoves provide excellent temperature control, allowing you to adjust the flame instantly. This precision is particularly valuable for tasks like simmering, where maintaining a consistently low heat is essential.
- Efficiency: Propane stoves are highly efficient, with minimal heat loss. They heat up quickly and distribute heat evenly across the cooking surface, reducing cooking times and energy consumption.
- Cost-Effective: Propane is often more cost-effective than electricity or natural gas for cooking. It offers a good balance between affordability and performance.
- Portability: Propane stoves are portable, making them ideal for outdoor cooking, camping, or emergencies. You can easily connect them to a propane tank and enjoy cooking wherever you need.
- Reliability: Propane is a reliable source of energy, even in areas with intermittent electrical service. You can depend on your propane stove to function consistently, regardless of power outages.
- No Electricity Required: Unlike some electric stoves that rely on electricity for ignition and control, propane stoves operate without electricity. This feature is valuable in emergencies when power is unavailable.
- Quick Heating And Cooling: Propane stoves heat up rapidly and cool down quickly when you turn off the flame. This responsiveness allows for efficient cooking and reduces the risk of food overcooking.
- Wide Range Of Options: Propane stoves come in various styles and sizes, from traditional stovetop ranges to portable camping stoves and outdoor grills. You can choose the one that best suits your cooking needs.
- Long Shelf Life: Propane is stored in tanks or cylinders, and it has a long shelf life when properly stored. This means you can have a reliable source of cooking fuel on hand for an extended period.
- Versatility: Propane stoves can accommodate a variety of cooking methods, from boiling and frying to baking and grilling. They offer versatility in the types of meals you can prepare.
- Safety Features: Modern propane stoves often come equipped with safety features like automatic shut-off valves and flame sensors, enhancing user safety.
- Environmental Benefits: Choosing propane as a cooking fuel supports environmental sustainability due to its lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced air pollution compared to some other fossil fuels.
Overall, propane stoves are known for their efficiency, convenience, and versatility. Whether you’re looking for an energy-efficient cooking solution for your home or a portable option for outdoor adventures, propane stoves offer a range of benefits that can enhance your cooking experience while minimizing environmental impact.
Final Verdict On Converting A Natural Gas Stove To Propane
So, converting a natural gas stove to propane is a task that requires careful consideration, attention to detail, and a commitment to safety.
This process involves adjusting the stove’s orifices, regulator, and burner components to accommodate the differences between natural gas and propane. When executed correctly, the conversion allows you to enjoy the benefits of using propane as a fuel source for cooking and heating.
However, it’s crucial to emphasize that converting a stove from one gas type to another is not a DIY project for the inexperienced. It should be undertaken by a qualified professional or technician who has the knowledge and expertise to ensure that the conversion is performed safely and effectively. Safety should always be the top priority when working with gas appliances.
Additionally, homeowners must be aware of local regulations and codes governing gas conversions. Complying with these regulations is essential to maintain safety and avoid potential legal issues.
FAQs
-
What Is The Primary Difference Between Natural Gas And Propane Stoves?
Natural gas stoves use methane from a utility provider, while propane stoves rely on stored propane in tanks. Propane offers greater portability and can be used in areas without natural gas infrastructure.
-
Can I Convert Other Gas Appliances To Propane?
Yes, many gas appliances can be converted to propane by following a similar process, but it’s essential to use the correct conversion kits and follow safety guidelines.
-
Is It Safe To Perform The Conversion Myself?
If you have the necessary skills and follow safety precautions, converting your stove to propane can be safe. However, if you’re unsure, it’s recommended to hire a professional.
-
How Often Should I Perform Maintenance On My Propane Stove?
Regular maintenance should be performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. This typically includes cleaning, inspection, and component replacement as needed.
-
Are There Any Government Regulations Regarding Gas Stove Conversions?
Regulations can vary by location, so it’s essential to check with local authorities or gas utility providers for any specific requirements or permits related to gas stove conversions.
🔧 Stove Expert | 🔥 Gas Guru | 🏠 DIY Enthusiast | 🎨 Painter Extraordinaire
John Davis is your go-to source for all things stoves, from expert repairs to maintenance tips. With a deep understanding of gas systems, including natural and propane, John ensures your kitchen stays cooking safely. His passion for DIY home and kitchen projects shines through his stunning paint transformations. Trust John to bring warmth and functionality to your home, one stove at a time.






Thank you for sharing these steps! As a propane delivery service in Albany, NY, we often get questions from customers about converting their natural gas stoves to propane. Your article does a fantastic job of outlining the process clearly and concisely. We appreciate the valuable information you provide on your website, and we’re sure our customers will find it helpful too!
Thank you, Propane Delivery Albany NY, for your kind words! I’am glad to hear that you found the article helpful. If you or your customers have any more questions about converting appliances to propane or any other topic, feel free to reach out. I’am always here to help!
First Fuel and Propane offers delivery of propane for both residential and commercial purposes in various counties including Albany, Schenectady, Saratoga, Columbia, Dutchess, Warren, Green, Washington, Rensselaer in the state of New York, as well as Berkshire County in Massachusetts.